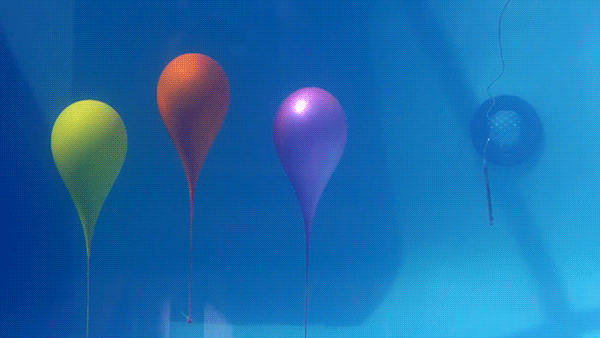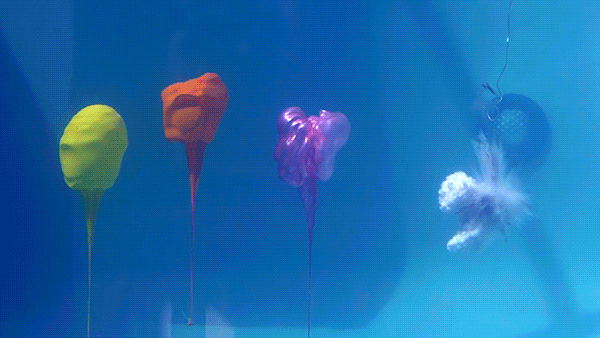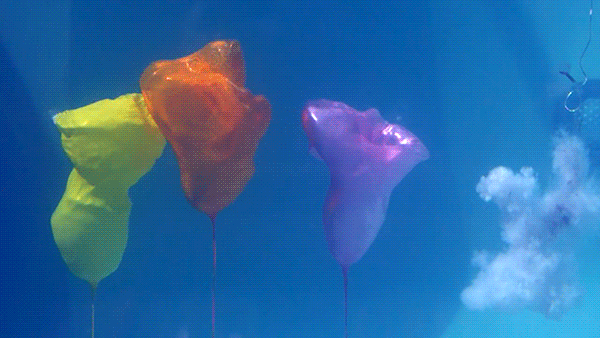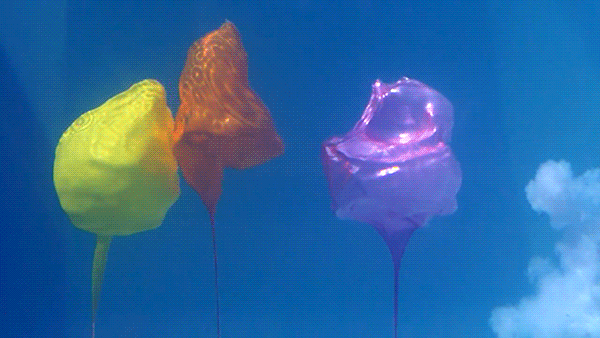22 April 2016
The saw-scaled viper ( Echis carinatus ) is a venomous viper species found in parts of the Middle East and Central Asia that is responsible for causing the most venom-related deaths in the world. While their venom isn’t the most toxic, they are extremely aggressive and are predominantly located in regions of the world without anti-venom extensive medical capabilities.
When a few drops of venom is introduced into a sample of blood, it immediately causes the rupturing of red blood cells (hemolysis) and triggers the coagulation cascade. This causes a clot to form and makes the blood thicken into a more jelly-like substance. In the body, a loss of blood flow can result in serious injury and death very quickly if left untreated.
Source: https://youtu.be/Q87UkykCbvI
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Venom #Snake #Poison #Viper #Toxic #Clotting #Blood #RedBloodCells #Hemolysis
View Original Post on Google+

20 April 2016
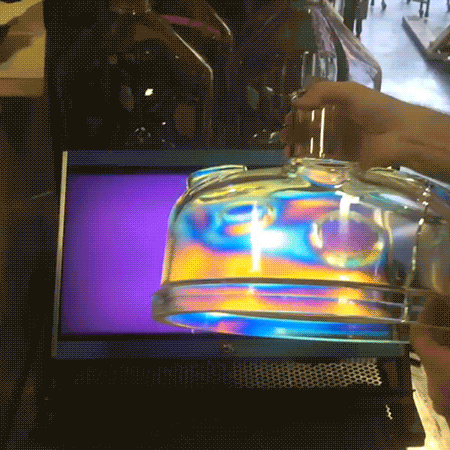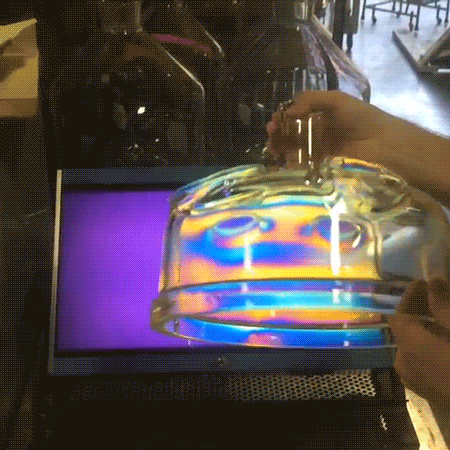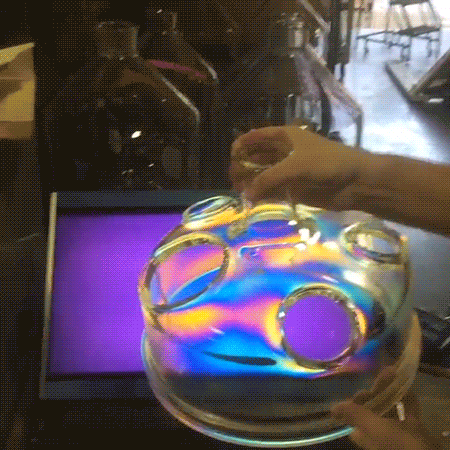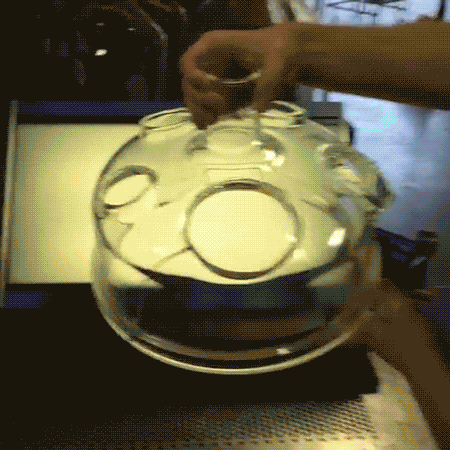
A polariscope allows for the visualization of internal stresses in an object using the polarization of transverse electromagnetic (light) waves. Here it is comprised of an LCD panel used as a source of linearly polarized light and a camera covered by a linear polarizer sheet oriented to block the polarized light.
Because different wavelengths (color) and polarizations of light propagate through a medium at different speeds (birefringence), the polarization axis of the light is rotated differently depending on color as it passes through the object. The resulting changes in polarization caused by the object allow the camera to image certain colors of light.
Since the internal stress in the glass object causes local variations in its birefringence properties, the image seen by the camera corresponds to these stresses. If the glass object had been rotated completely around to properly image the crack, there would have been little color surrounding it.
Source: https://www.instagram.com/p/4bvG3oognr/
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Polariscope #Polarizer #Light #Wave #Electromagnetic #Polarization #Glass #Stress #Strain #Mechanical #Materials #Filter #Reactor #Birefringence #Rotation
View Original Post on Google+
19 April 2016
Researchers in Norway have developed the Eelume, a sea-snake inspired mechanical robot designed to reside on the sea floor to monitor and adjust underwater equipment. Such tasks are difficult for humans to perform given the location yet would be easily accessible for a small mobile robot. The robot propels itself using the sidewinding motion used by snakes on both land and in water.
Source: https://youtu.be/sIpIAbWo_2A
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Engineering #Mechanical #Robot #Robotics #Sea #Snake #Biology #Nature
View Original Post on Google+

15 April 2016
Researchers at Rice University have discovered that the strong field emitted by a Tesla coil causes carbon nanotubes to self-assemble into long wires. This phenomenon has been named “teslaphoresis” and could help pave the way for the scalable assembly of nanotubes.
In addition to forming a circuit between two LEDs, the nanowires are also capable of harvesting energy from the emitted electromagnetic field to illuminate them. While the field from the Tesla coil is currently limited to only a few feet, patterned surfaces and multiple coils could create much more complex nanowire patterns.
Source: https://youtu.be/w1d0Lg6wuvc
Learn More: http://goo.gl/7rABKo
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Nanotubes #Carbon #Teslaphoresis #Tesla #Electricity #Wire #Nanowire #SelfAssembly #Physics #TeslaCoil #Current
View Original Post on Google+

14 April 2016
When a direct electric current is applied across a solution of stannous chloride (SnCl2) an otherwise nonspontaneous chemical reaction called electrolysis takes place. The stannous chloride dissociates into Tin(II) and chloride (Cl-) ions which serve as the electrolyte for the redox reaction. At the cathode, Tin(II) is oxidized into Tin(IV), which forms the metal crystals spreading across the beaker. At the anode, oxygen gas (O2) is produced.
If the metal were allowed to grow all the way between the cathode and anode, it would short-circuit the electrolytic solution and risk damaging an unprotected power supply.
Source: https://youtu.be/r-YbQN_twpw
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Electrolysis #Tin #StannousChloride #ChemicalReaction #Chemical #Reaction #Chemistry #Electrochemistry #Crystal #Electricity #Solution #Electrolyte
View Original Post on Google+

12 April 2016
Water is highly incompressible , which means it does not readily change volume in response to a change in pressure. This means that a shockwave from an underwater explosion does not dissipate quickly like it does in air and actually travels much further.
In this demonstration, the three balloons are filled with air and highlight the shockwave passing through the water. Because air is a compressible fluid, the balloons are significantly deformed by the shockwave.
Unlike the demonstration of a person diving underwater to avoid gunfire, escaping an explosion this way would likely result in death. While the majority of the human body is water that the shockwave would leave unharmed, there are plenty of compressible parts (e.g. air filled lungs) that would be heavily damaged by the rapid change in pressure.
Source: https://youtu.be/W4DnuQOtA8E
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Liquid #Water #Explosion #Compressibility #Balloons #Air #Physics #Physiology #Grenade #Detonation #Pressure #Volume #Material
View Original Post on Google+
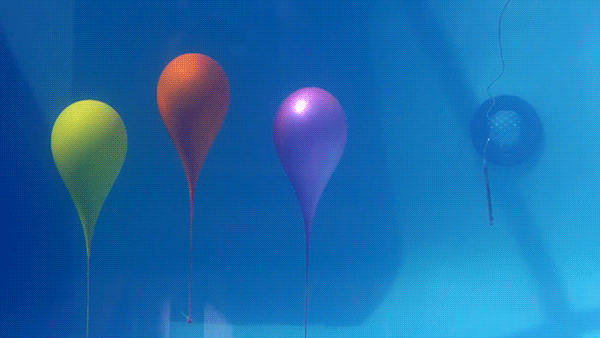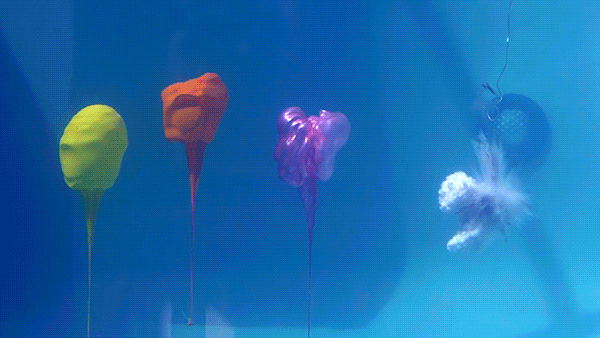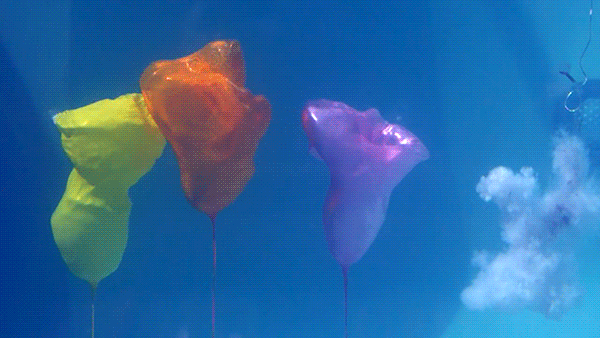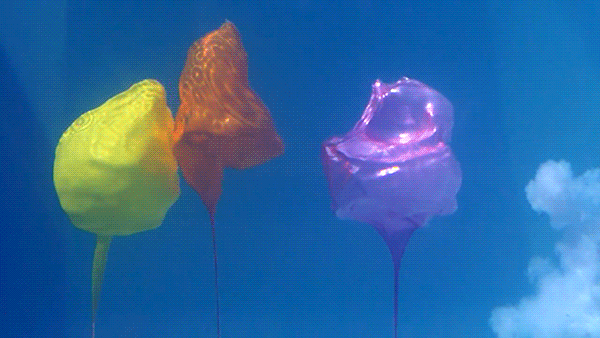
11 April 2016
Composite metal foams are being developed for use in ballistic armor because of their light weight and high impact energy absorption capabilities. This particular layered design absorbed 60-70% of the total kinetic energy of the projectile (7.62x63 mm M2 Armor Piercing) with less depth penetration and backplate deformation than the standards defined by the U.S. National Institute of Justice. The redirection of the kinetic energy results in the bullet shattering into pieces upon impact on the surface.
Source: https://youtu.be/lWmFu-_54fI
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Metal #Foam #MetalFoam #Bullet #ArmorPiercing #Armor #Piercing #MechanicalEngineering #MaterialScience
View Original Post on Google+
8 April 2016
SpaceX successfully landed the booster stage of its Falcon 9 rocket today on the droneship Of Course I Still Love You in the Atlantic Ocean. This is the fifth attempt of an at-sea landing by the company and the first to not end with RUD (Rapid Unscheduled Disassembly). The Falcon 9 rocket launched the Dragon spacecraft to low Earth orbit to deliver critical cargo to the International Space Station as part of CRS-8.
Fun Fact: SpaceX has named its two floating landing platforms ( Just Read the Instructions and Of Course I Still Love You ) after spaceships from Iain M. Banks’ Culture series.
Source: https://youtu.be/7pUAydjne5M (SpaceX)
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #SpaceX #ElonMusk #Rocket #Dragon #CRS8 #Spaceship #Booster #Landing #Barge #Culture #Sea #Ocean #Reusable
View Original Post on Google+

7 April 2016
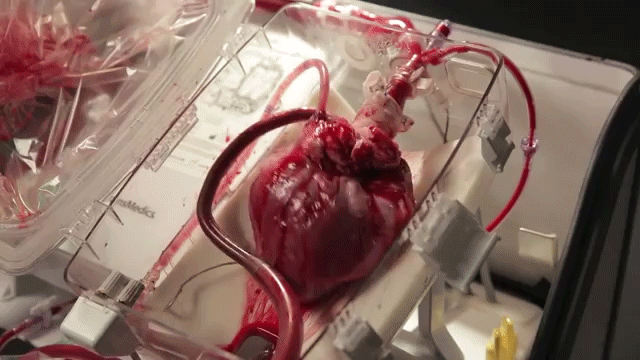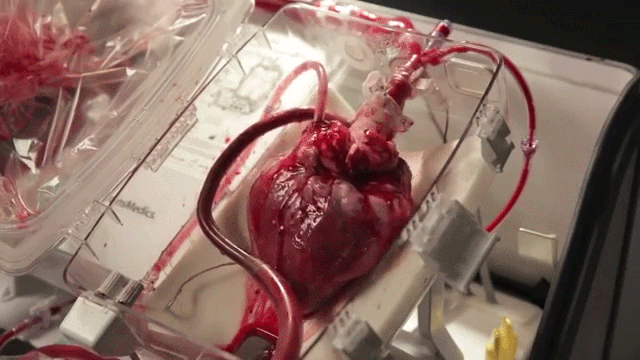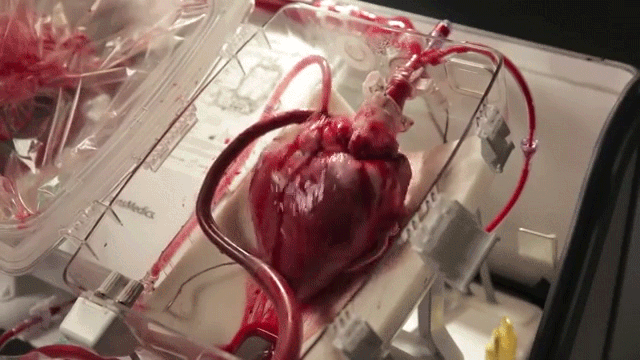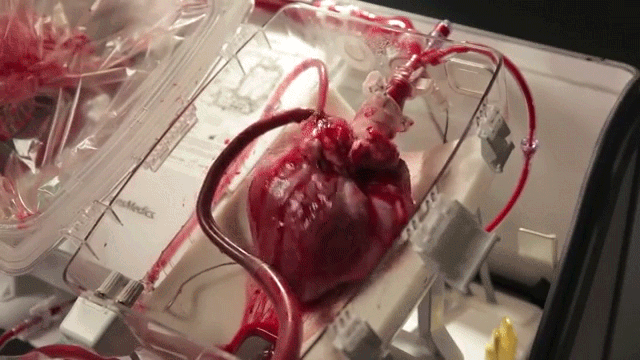
The current best-practice for the transportation of donor hearts between hospitals is to put it on ice inside a store-bought cooler. This severely limits the time window for performing the transplant (~4 hours) and introduces unnecessary risks for an already complex surgical procedure.
The Transmedics Organ Care System being tested at the University of Michigan is an investigational medical device that keeps the heart warm and beating outside the body. This allows for much longer transportation distances and allows the heart to be perfused with oxygen and nutrients until the patient is ready to receive it.
Source: http://goo.gl/vAR1F8
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Medicine #Heart #Transplant #Pumping #Beating #Biomedical #Organ #Donor #Healthcare #Surgery
View Original Post on Google+
5 April 2016
Chlorosulfonic acid (or sulfurochloridic acid) is an inorganic compound with the formula HSO3Cl. It is a strong oxidizer and an extremely dangerous acid. It reacts violently with water to produce sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, seen here as vapors fuming from the flower. Contact with bare skin would produce severe burns and inhalation can be fatal.
Source: https://youtu.be/yHXW9Il90VA
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Acid #Chlorosulfonic #Daffodil #Flower #Inorganic #Reaction #Chemistry #Chemical
View Original Post on Google+