10 June 2017
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by a living organism that is most widely found amongst marine animals and most famously in fireflies. The primary chemical reaction that occurs is the mixture of the light-emitting pigment luciferin and the enzyme luciferase. The enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of luciferin, which results in the release of blue-green light.
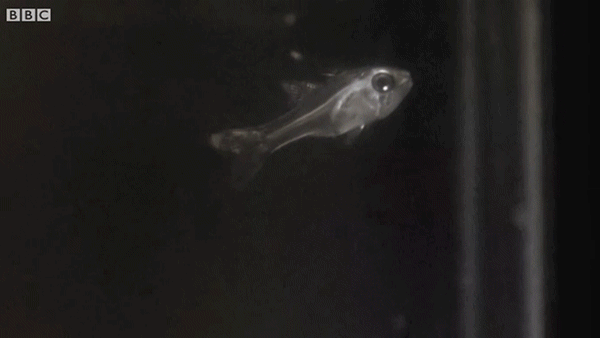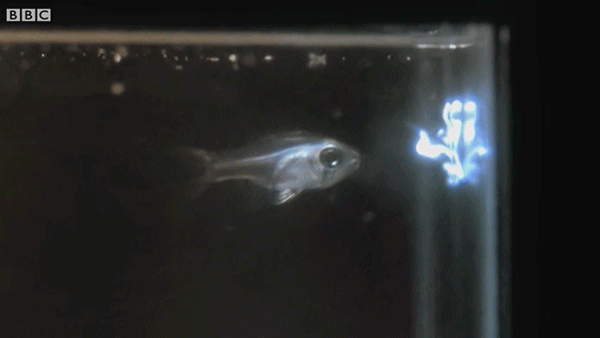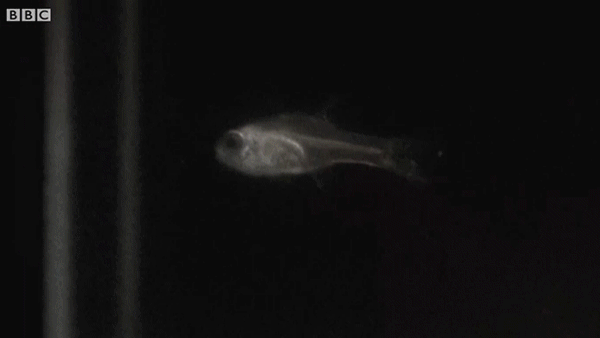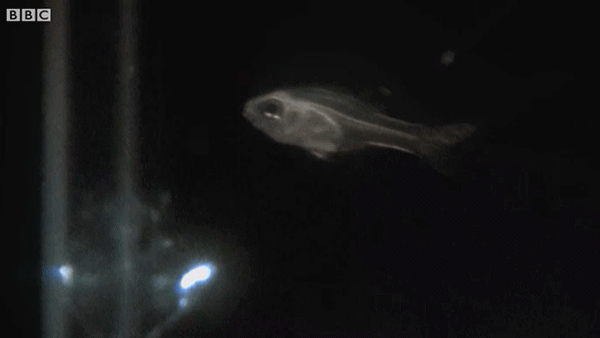
Ostracods, also known as seed shrimp, are small crustaceans found across a wide range of water environments. A subset of ostracods possess light organs used in bioluminescent predation defense. When attacked, the small plankton produce a blinding cloud of light that startles the predator, allowing the ostracod to escape. Here, cardinalfish can be seen eating and then expelling ostracods after they employ their bioluminescent defensive technique.
Source: http://www.bbc.co.uk/nature/28838200 (BBC)
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Bioluminescence #Defense #SelfDefense #Predator #Predation #Prey #Nature #Biology #Fish #Ostracod #Shrimp #Luminescence #Light
View Original Post on Google+
3 June 2017
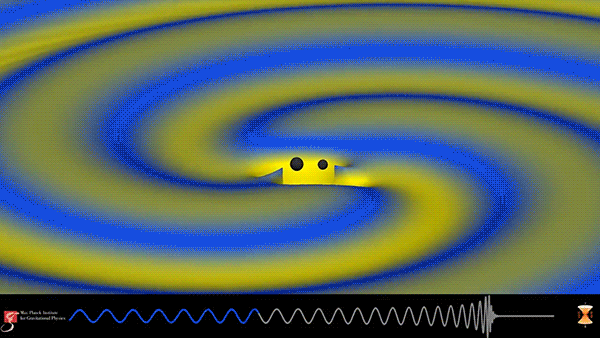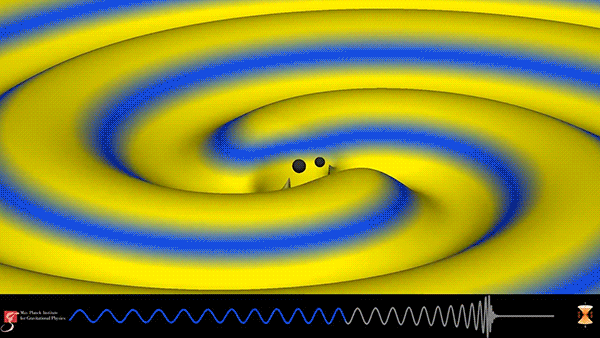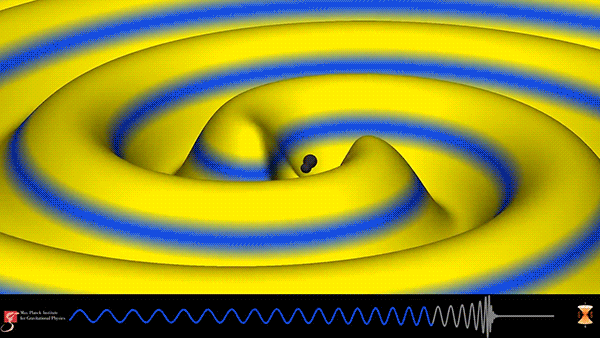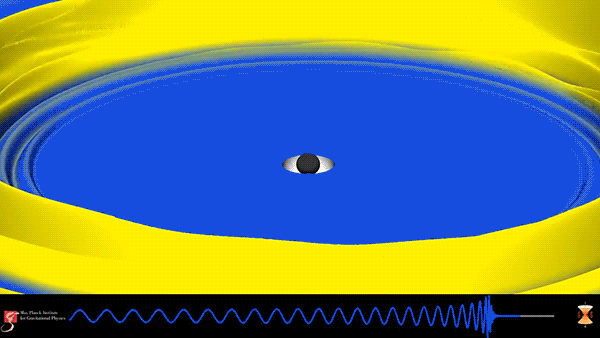
After being offline for much of 2016 undergoing upgrades, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) has made its third observation of the ripples in spacetime known as gravitational waves. On January 4, 2017 at 10:11:58.6 UTC, LIGO detected the merger of two immense black holes over 3 billion light-years away from the Earth. The resulting black hole has a mass about 49 times that of our sun and during the final moments released more energy in the form of gravitational waves than all the stars in the observable universe.
This simulation from the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics shows the binary black-hole coalescence detected by LIGO. The waveform at the bottom depicts the gravitational wave, which starts with a frequency of about 25Hz. As the black holes spiral closer and closer together, the frequency and amplitude of the gravitational waves increase until the merger occurs and ends the perturbation in spacetime.
Source: https://goo.gl/5oqnJn
LIGO’s first discovery: https://goo.gl/XBCPbe
How LIGO works: https://goo.gl/NDO7VX
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #LIGO #GravitationalWave #Gravitational #Wave #Einstein #GeneralRelativity #General #Relativity #Physics #Astronomy #Astrophysics #BlackHole #EventHorizon #Animation
View Original Post on Google+
27 May 2017
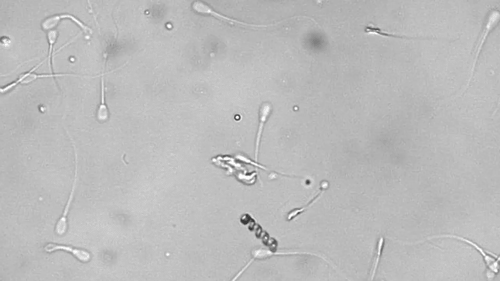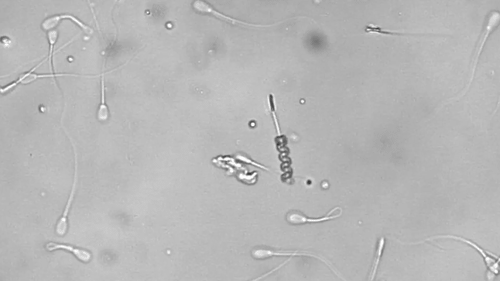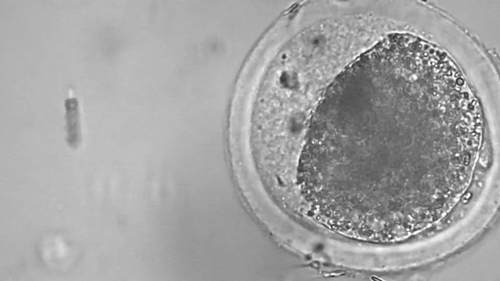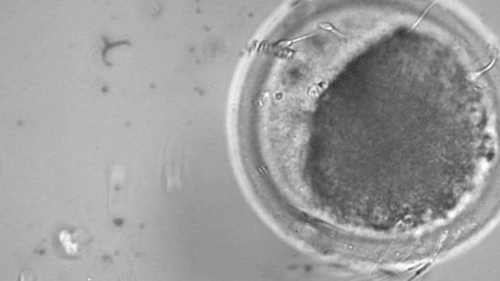
Science fiction has long written of using microscopic robots to perform medical tasks within the human body. These tiny machines can readily access vasculature, tissue, and organs without the need for invasive surgery. While we’re still a long way from autonomous robots swimming around in our bloodstream, scientists are making significant progress.
This helix-shaped micromotor is powered by an external magnetic field and demonstrates its cargo-carrying capacity by assisting with artificial fertilization. The micromotor envelopes an immotile bovine sperm and carries it to an egg cell. The spinning of the helix mimics the motion of flagella commonly used by many microorganisms for locomotion.
Source: https://goo.gl/5w14Rb (Nature)
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Microbot #Micromotor #Micro #Biology #Fertlization #Artificial #Cell #Sperm #Egg #Gamete #Inseminiation
View Original Post on Google+
20 May 2017
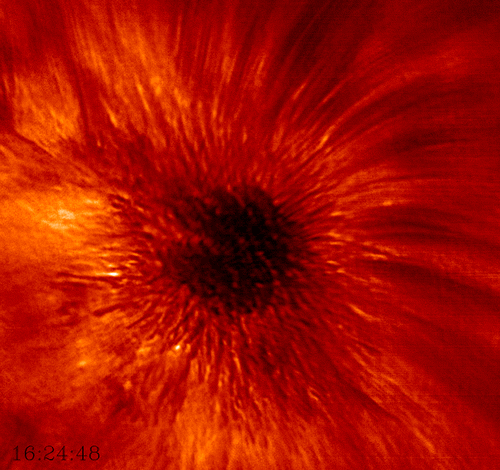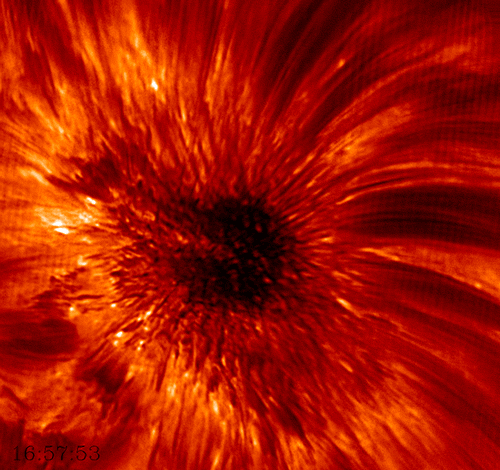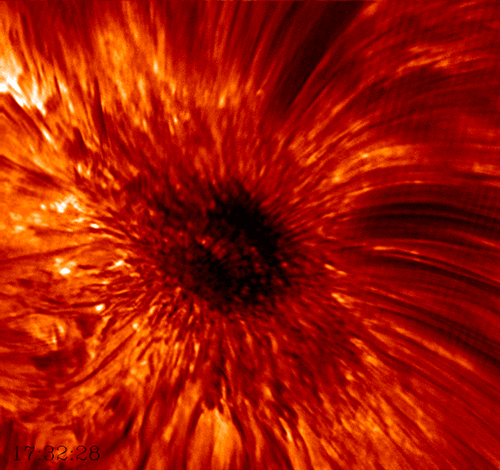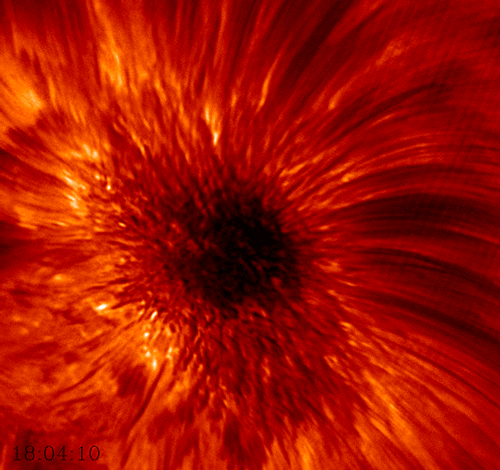
Sunspots were first documented by humans around 800 BC when the Chinese noticed dark blemishes on the Sun. The first telescopic observations were carried out in late 1610 by the English astronomer Thomas Harriot. However, it took until 1613 for Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei to demonstrate that sunspots were actually located on the surface of the Sun and not caused by planetary transits. While we now know that sunspots are compact, concentrated magnetic fields that appear dark because the high magnetic field flux inhibits convection, they still remain one of the greater mysteries of astronomy.
The diameter of sunspots can range from a few kilometers to larger than the planet Jupiter (140,00km). The temperature of the sunspot’s umbra , the dark center region, is only about 2,700-4,200°C compared to the 5,500°C solar surface.
This high-resolution imagery of a sunspot was acquired by the Big Bear Solar Observatory in California using their 1.6m solar telescope. This was the first detailed view of the rapidly rotating convective plasma within the umbra. It also depicts the periodic shockwaves generated by sunspots that rocket through the Sun ‘s chromosphere at speeds up to 45,000mph.
Source: https://goo.gl/tjYSzt (BBSO)
Learn More: http://bbso.njit.edu/
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Sun #Sunspot #Solar #Observatory #BigBear #NIJT #BBSO #Telescope #Plasma #Star #Fusion
View Original Post on Google+
13 May 2017
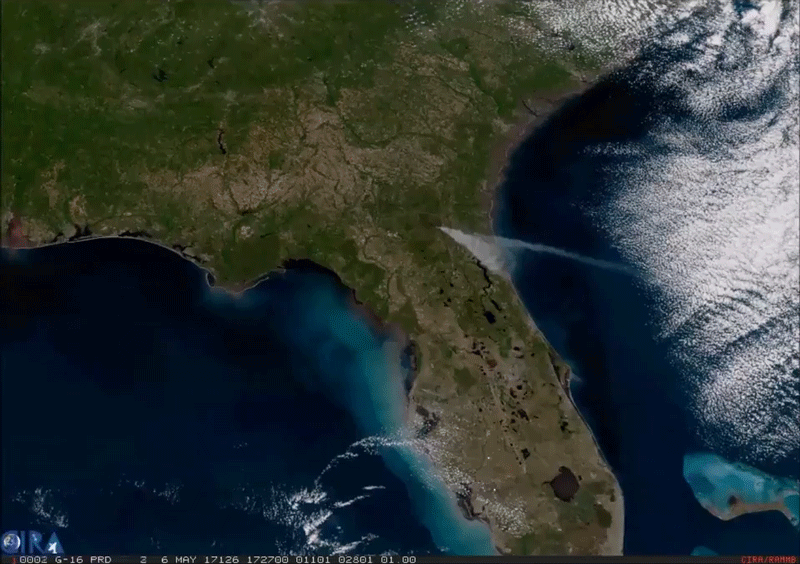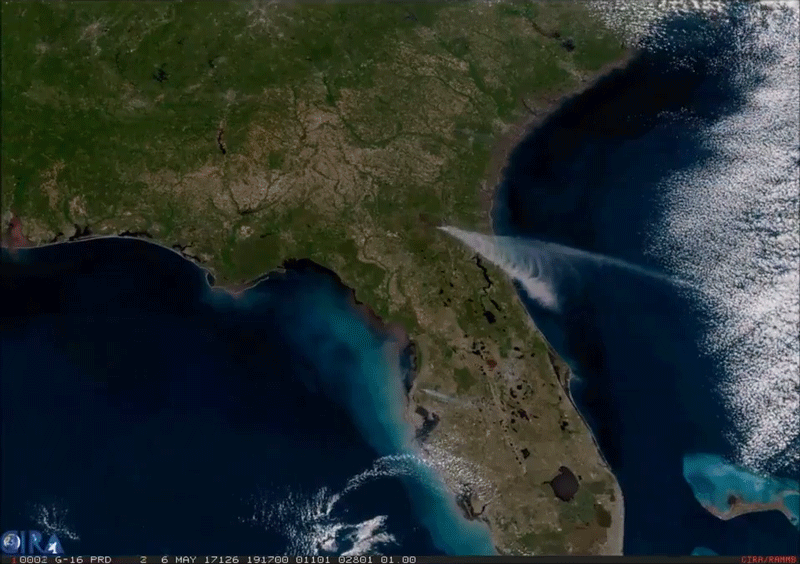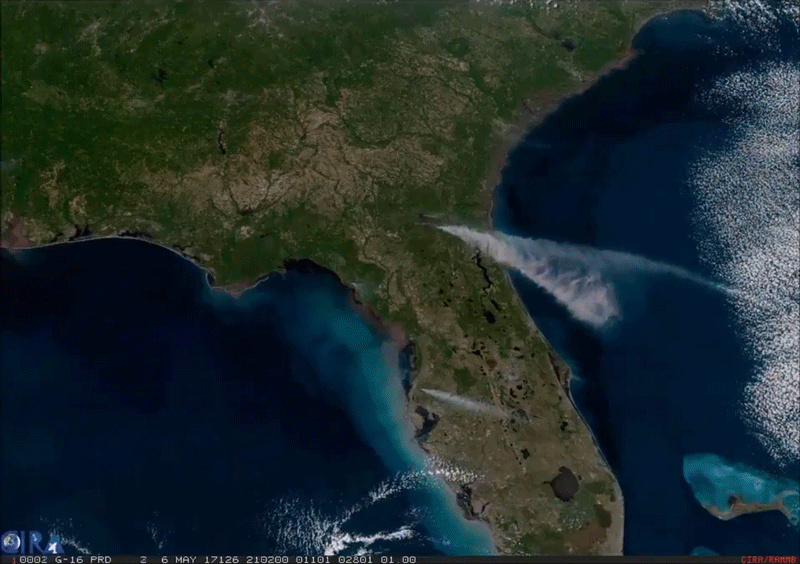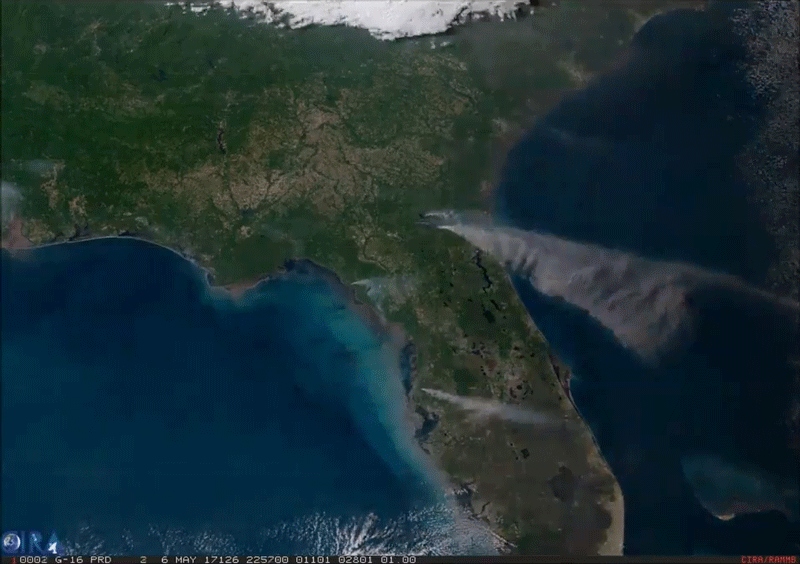
This imagery of smoke from an enormous wildfire in southeast Georgia was captured by the American GOES-16 weather satellite. It is the first of the next generation of geosynchronous environmental satellites jointly operated by NASA and NOAA that will provide atmospheric and surface measurements of Earth. Data from the GOES system is used for weather forecasting, severe storm tracking, space weather monitoring, and meteorological research.
GOES-16 was launched from Cape Canaveral on November 16, 2016, and entered geostationary orbit 26,200 miles above the surface of the Earth where it surveils the Western hemisphere. The satellite is capable of viewing the Earth across 16 spectral bands and provides 4x the spatial resolution and more than 5x faster coverage than its predecessors. The satellite also contains instrumentation for mapping lightning on Earth, imaging the ultraviolet spectrum of the Sun, measuring solar emissions, and tracking the outer magnetosphere of the planet.
Source: https://goo.gl/y16LuR (NOAA)
More GOES-16 Imagery: https://goo.gl/iNTz9L
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #NASA #NOAA #GOES #GOES16 #Wildfire #Florida #Georgia #Smoke #Satellite #Image #EarthScience #Climate #Research
View Original Post on Google+
6 May 2017
Triboluminescence is an optical phenomenon that generates light through the breaking of chemical bonds in a material when it is pulled apart, ripped, rubbed, scratched, or crushed (fractoluminescence). An exact understanding of how the process works has yet to be established. The current theory involves electrical charge separation that results in ionization of the surrounding air, which produces the flash of light.
Mint-flavored Life Saver candies are an easy way to visualize this phenomenon with the naked eye. Crushing them with a hammer (or your teeth) in a dark room will generate bright blue sparks. This light is actually generated by a two-step process involving fluorescence, which is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed another wavelength of light. The light released by triboluminescence is ultraviolet and therefore invisible to the human eye. However, the wintergreen oil used in mint flavoring is fluorescent, and converts the invisible ultraviolet light into visible blue light.
I highly recommend watching the source video from +SmarterEveryDay to see more slow motion footage of Life Savers being hammered and shot with a pellet gun.
Source: https://youtu.be/tW8q_JfmcbU (Smarter Every Day)
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Triboluminescence #Light #Luminescence #Mechanical #Chemical #Bond #Photons #Energy #HighSpeed #SlowMotion #SlowMo #LifeSaver #Lightning #SmarterEveryDay
View Original Post on Google+

29 April 2017
Prince Rupert’s Drops are beads of toughened glass created by dipping molten glass into cold water, which causes it to solidify into a tadpole-shaped droplet. As the glass cools from the outside in, it produces significant compressive stresses on the surface and tensile stresses at the core of the drop. The spherical shape of the bulbous head gives the glass enormous strength, such that it can be struck with a hammer without breaking. However, the tail is extremely fragile and causes the entire droplet to explosively shatter when cracked.
The +SmarterEveryDay YouTube channel has a series of videos examining the behavior of Prince Rupert’s Drops using high-speed cameras. Here a .38-caliber bullet can be seen disintegrating upon impact with the head of the droplet without damaging the glass.
Source: https://youtu.be/F3FkAUbetWU (Smarter Every Day)
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Glass #Bullet #Impact #Stress #Mechanical #Strength #Stress #Molten #Drop #Droplet #PrinceRupert #HighSpeed #Camera #SmarterEveryDay
View Original Post on Google+

22 April 2017
The blue whale is the largest animal known to have existed on the planet Earth and can reach lengths of almost 100 ft and weigh over 400,000 lbs. Despite their enormous size, blue whales consume a diet primarily consisting of krill, a ocean small crustacean near the bottom of the food chain. A whale feeds by lunging towards a group of krill, engulfing the animals and a large amount of water in its mouth. A specialized filter system known as a baleen plate allows the water to be squeezed back out of the mouth, leaving only the krill behind. An adult blue whale can consume up to 40 million krill in a single day.
New research from Oregon State University has found that blue whales will not put energy into feeding on low-reward prey patches. Aerial drones were used to track behavior during surface feeding and discovered that the whales would avoid smaller krill groups in favor of larger ones. Here a blue whale can be seen consuming an enormous patch of krill in a single lunge.
Source: https://goo.gl/jjG8OF
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #BlueWhale #Blue #Whale #Krill #Ocean #Feeding #Crustacean #Mammal #Sea #Life #Nature #Oceanography #Drone
View Original Post on Google+

8 April 2017
Kingfishers are small, brightly colored birds classified within the order Coraciiformes , which is a misnomer because it means “raven-like.” There are over 90 different species of kingfishers located across the planet and they share similar physical characteristics: large heads, long, sharp, pointed beaks, and short legs. While famous for hunting fish, kingfishers actually consume a wide range of prey including insects, amphibians, crustaceans, molluscs, and spiders.
This slow-motion shot depicts a kingfisher performing its signature dive into water in search of small fish. Although unsuccessful, the bird emerges from the water with a twisting motion in order to return to flight.
Source: https://vimeo.com/107714608 (PCO)
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Nature #Biology #SlowMotion #Kingfisher #Bird #Fish #SlowMo #HighSpeed #Raptor
View Original Post on Google+

5 April 2017
Last Thursday, +SpaceX successfully re-launched and landed the first stage of a Falcon 9 rocket on the drone ship Of Course I Still Love You. This is the first re-flight of an orbital class rocket in human history (sorry Blue Origin, you don ‘t count) and a major milestone for the space industry. The ability to re-use the most expensive part of a rocket promises to drastically reduce the cost of future spaceflight.
Source: https://www.instagram.com/p/BSfJDjMFzwR/ (SpaceX)
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #SpaceX #ElonMusk #Rocket #Falcon9 #Rocket #Reflight #Landing #Satellite #Mission #SES #Landmark
View Original Post on Google+











