The high spatial and temporal coherence of lasers allows them to be precisely focused into small spots, making them ideal for optical cutting and lithography applications. While most people are familiar with continuous wave (CW) lasers that constantly emit the same amount of light, pulsed lasers can be used to achieve significantly higher peak power by emitting discrete pulses of light.
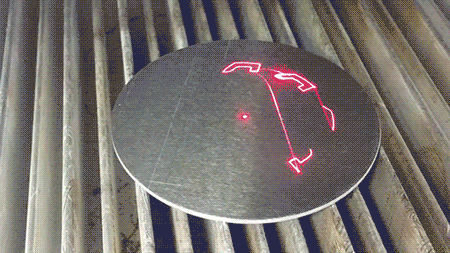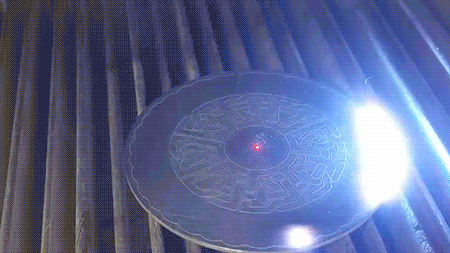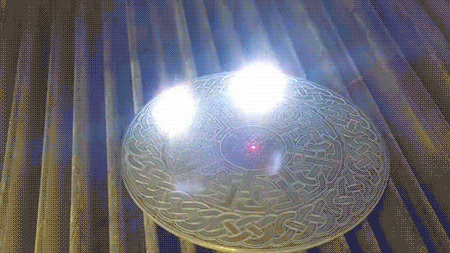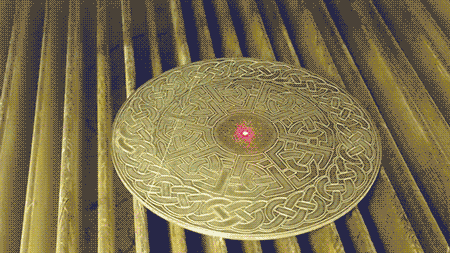
Here a pulsed near-infrared laser can be seen engraving a metal plate with a complex design in real time. A preliminary red laser (635 nm) is used to validate the positioning of the pattern on the surface before the primary laser (1064 nm) begins the engraving process.
Source: https://youtu.be/iKTR9bl-T00 (Z-Tech)
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Laser #Engraving #Engrave #Light #Pulse View Original Post on Google+