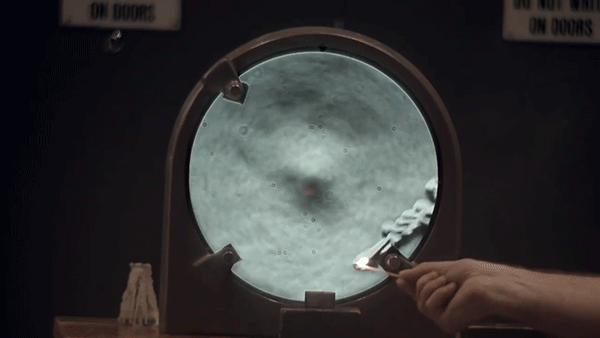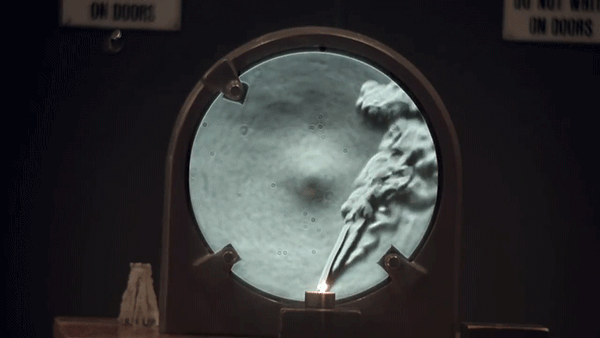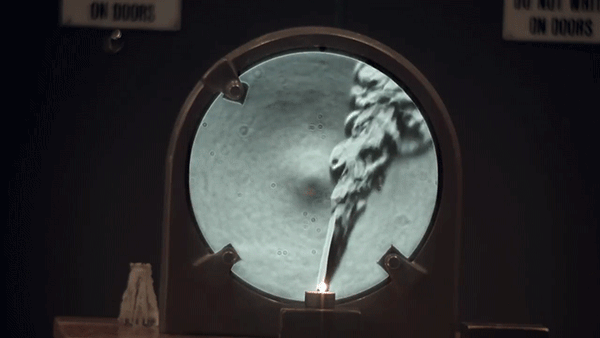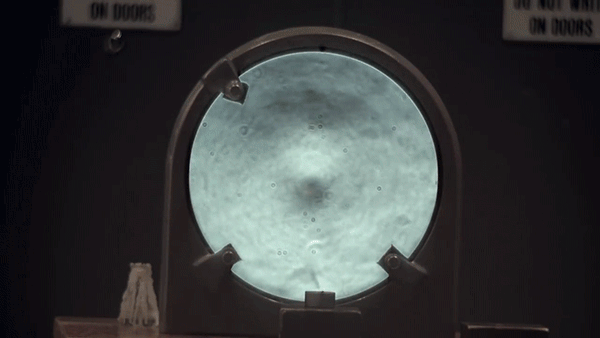
Schlieren photography is an optical imaging technique that allows for the visualization of small differences in index of refraction. This makes inhomogeneities, such as temperature, pressure, or composition, in normally transparent materials easily observable with a camera.
Hot air rising upwards from an open flame results in billowing clouds when imaged with this technique. This occurs because hot air refracts light slightly differently than the cooler air around it (i.e. hot air has a different index of refraction). A schlieren camera is extremely sensitive to the resulting changes in optical path caused by these variations.
The schlieren phenomenon was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 but the current technique was not developed until the mid 19th century by the physicists Jean Bernard Léon Foucault and August Toepler. It was originally used to detect flaws in glass used for making lenses but has since been adopted for studying aerodynamics and fluid flow.
Source: https://youtu.be/mLp_rSBzteI (Harvard)
Learn More: https://youtu.be/4tgOyU34D44
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #Schlieren #Photography #Optics #Index #Refraction #Air #Optical #Flame #Physics View Original Post on Google+