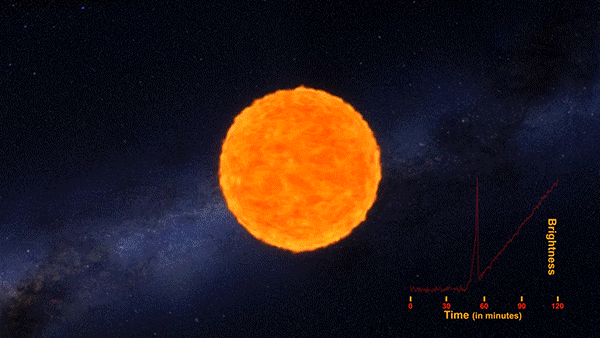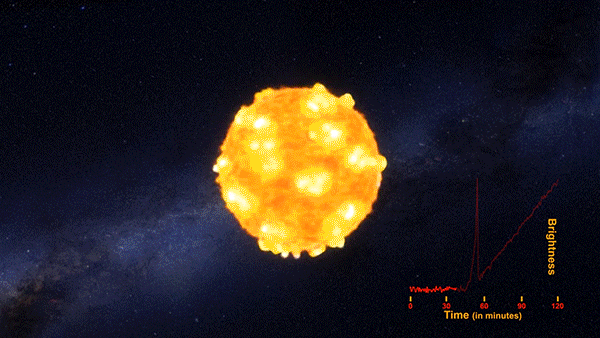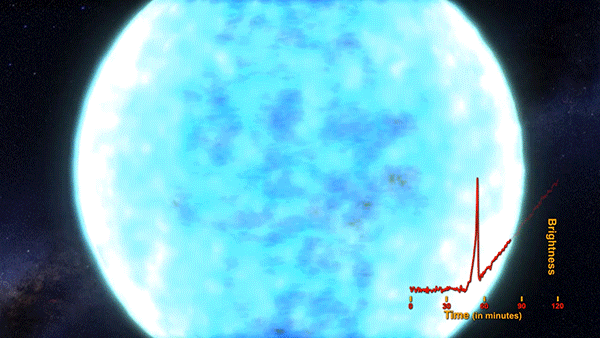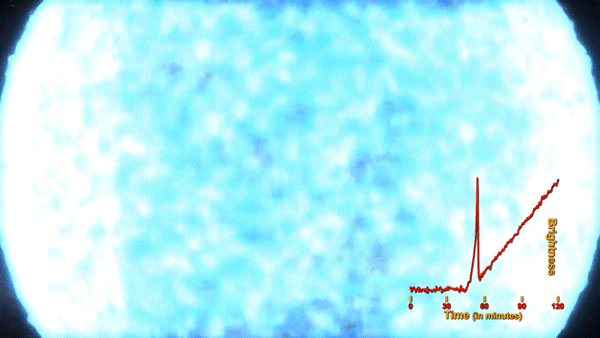
The flash of an exploding star’s shockwave, called a shock breakout, has been captured for the first time by NASA’s planet-hunting Kepler space telescope. An analysis of three years worth of data covering 500 galaxies and 50 trillion stars revealed the supernova of KSN 2011d. The red supergiant star was an estimated 500x the size of our Sun and located around 1.2 billion light years away.
The shock breakout, seen as an intense bright flash that preceded the rapid explosion of the star fits the theorized behavior of a Type II star’s death. This animation depicts the supernova and the incredibly fast speed at which it expands.
The study of supernova is vital to understanding the Universe since Iron (Fe) is the heaviest element that can be formed via nucleosynthesis in the cores of stars. All heavier elements were created during the cataclysmic supernova death throes of stars.
Source: http://goo.gl/CE7xsf (NASA)
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #NASA #Kepler #Satellite #Telescope #Supernova #Star #Explosion #Breakout #Shock #Light #Space #Discovery View Original Post on Google+