The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) is a large-scale physics experiment designed to detect gravitational waves predicted by Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity. There are two facilities located in Livingston, LA and Hanford, WA.
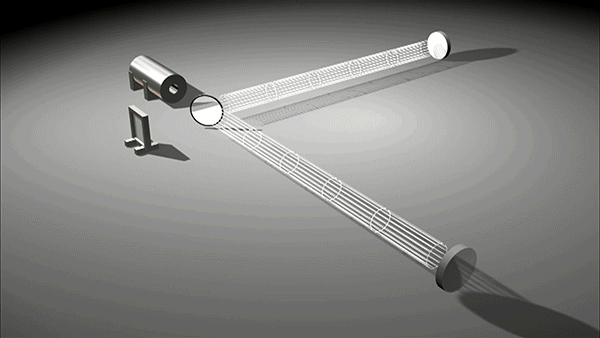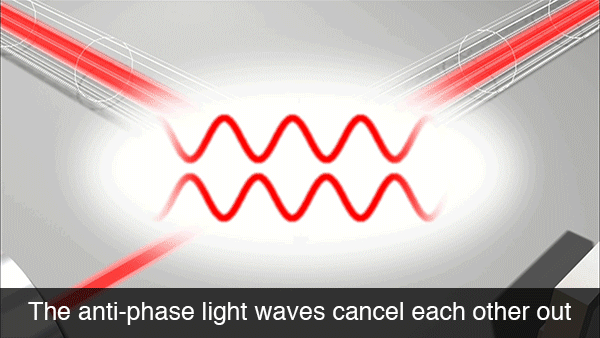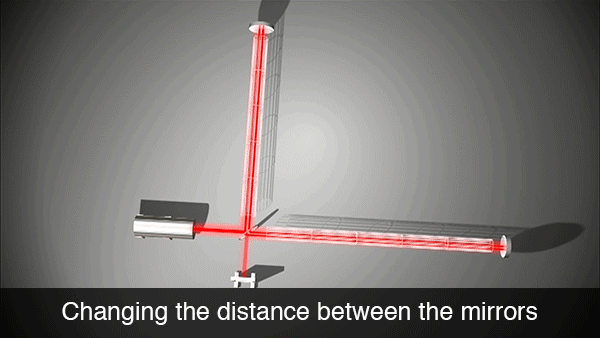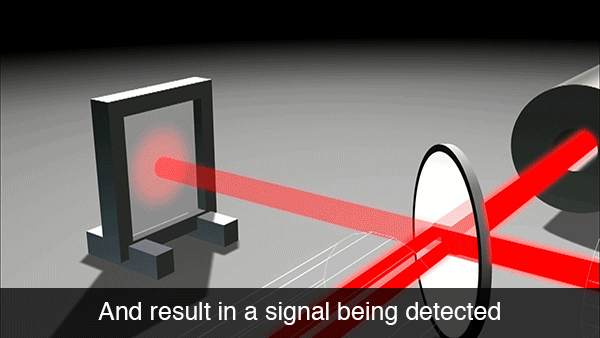
As the name implies, LIGO uses a technique called laser interferometry to detect the miniscule effects of a gravitational wave. A laser beam is split into two beams and the phase of one beam inverted relative to the source. The two laser beams are relayed down 4km tubes where they are reflected off a mirror. Because the two laser beams are anti-phase (phases are 180° apart), they cancel each other out via destructive interference and no signal is detected.
However, if a gravitational wave is passing by, it will stretch and compress the total travel length of the two laser beams. This means the two lasers are no longer anti-phase and will produce a detectable signal via their constructive interference.
For the gravitational wave detected on September 14, 2015, by LIGO, the distortion to the path length was approximately 1/1000th the diameter of a proton. This makes LIGO one of the most sensitive devices ever built by humanity.
Source: http://www.einsteinsmessengers.org/index.htm
#ScienceGIF #Science #GIF #LIGO #GravitationalWave #Laser #Interferometer #Physics #Detector #Phase #Light #Astronomy #Discovery View Original Post on Google+